- 14 Oct
- 2025
HYBRID LONG SHORT TERM MEMORY – MULTILAYER PERCEPTRON FRAMEWORK UNTUK MENINGKATKAN PREDIKSI PENJUALAN
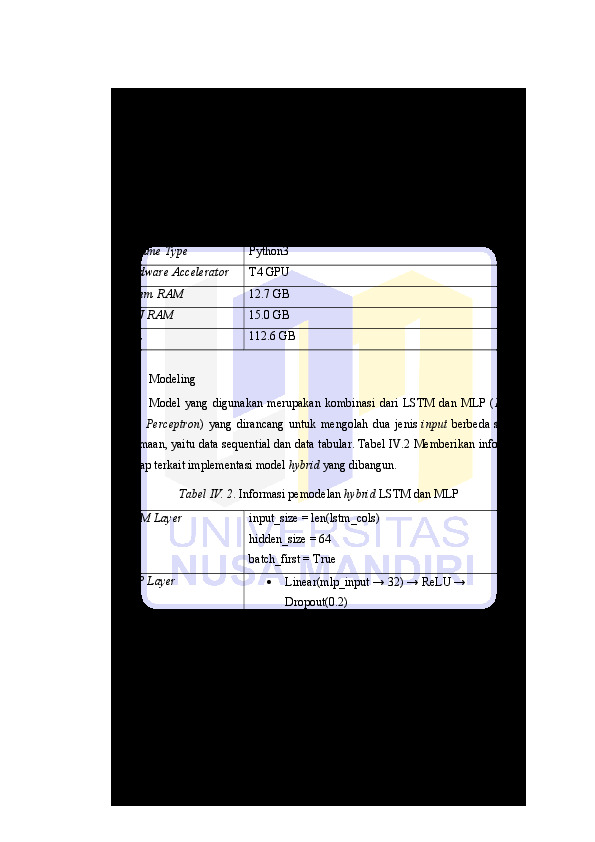
Penelitian ini mengembangkan model deep learning hibrida berbasis Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) dan Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) untuk memprediksi penjualan mingguan ritel. Model ini memanfaatkan LSTM untuk menangkap pola urutan waktu (time dependent). Namun LSTM memiliki keterbatasan pada poal atau kejadian yang tidak terikat waktu. Maka MLP dimanfaatkan untuk memproses fitur time independent untuk melengkapi konteks atau kejadian yang tidak tertangkap dengan baik oleh LSTM. Dataset Walmart Recruiting Store Sales Forecasting yang digunakan telah melalui proses rekayasa fitur dan pra-proses sebelum digunakan dalam pelatihan dan pengujian model. Evaluasi kinerja dilakukan menggunakan lima metrik, yaitu Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), Mean Squared Error (MSE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), dan koefisien determinasi (R²). Model LSTM-MLP menunjukkan performa terbaik dengan nilai MSE sebesar 14.07, RMSE sebesar 3.39, MAE sebesar 2.39, dan MAPE sebesar 12.39, serta R² mendekati 1.00. Kinerja model ini mengungguli model-model lain seperti MLP, GRU, dan Transformer dalam hal prediksi penjualan. Hasil ini menunjukkan bahwa arsitektur gabungan LSTM-MLP mampu menangkap kompleksitas pola penjualan secara efektif dan memberikan prediksi yang akurat dan stabil. Model ini potensial untuk diterapkan dalam sistem pendukung keputusan pada sektor ritel guna meningkatkan akurasi estimasi permintaan serta efisiensi perencanaan logistik dan stok.
Unduhan
REFERENSI
[1] L. Eglite and I. Birzniece, “Retail Sales Forecasting Using Deep Learning: Systematic Literature Review,” Complex Systems Informatics and Modeling Quarterly, no. 30, pp. 53–62, Apr. 2022, doi: 10.7250/csimq.2022-30.03.
[2] C. Wang, “Stock price forecasting by ARIMA, linear regression, LSTM and decomposition linear models,” Applied and Computational Engineering, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 61–68, Apr. 2024, doi: 10.54254/2755-2721/55/20241572.
[3] Y. Liu, “Sales Forecasting Based on Transformer-LSTM Model,” Highlights in Science, Engineering and Technology, vol. 85, pp. 776–782, Mar. 2024, doi: 10.54097/qdavzg31.
[4] I. Sonata and Y. Heryadi, “Comparison of LSTM and Transformer for Time Series Data Forecasting,” in 2024 7th International Conference on Informatics and Computational Sciences (ICICoS), IEEE, Jul. 2024, pp. 491–495. doi: 10.1109/ICICoS62600.2024.10636892.
[5] Y. Sun and T. Li, “A transformer-based framework for enterprise sales forecasting,” PeerJ Comput Sci, vol. 10, pp. 1–14, 2024, doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2503.
[6] R. Murugesan, E. Mishra, and A. H. Krishnan, “Forecasting agricultural commodities prices using deep learning-based models: basic LSTM, bi-LSTM, stacked LSTM, CNN LSTM, and convolutional LSTM,” International Journal of Sustainable Agricultural Management and Informatics, vol. 8, no. 3, p. 242, 2022, doi: 10.1504/IJSAMI.2022.125757.
[7] S. Sautomo and H. F. Pardede, “Prediksi Belanja Pemerintah Indonesia Menggunakan Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM),” Jurnal RESTI, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 99–106, Feb. 2021, doi: 10.29207/resti.v5i1.2815.
[8] H. Li and D. Wei, “Prediction based on traditional network prediction model and LSTM deep neural network model,” in Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Computing, Networks and Internet of Things, New York, NY, USA: ACM, May 2023, pp. 726–730. doi: 10.1145/3603781.3603910.
[9] S. Gyamerah and D. R. Korda, “Prediction of Stock Market Returns using LSTM Model and Traditional Statistical Model,” Int J Comput Appl, vol. 183, no. 37, pp. 57–61, Nov. 2021, doi: 10.5120/ijca2021921773.
[10] V. Sohrabpour, P. Oghazi, R. Toorajipour, and A. Nazarpour, “Export sales forecasting using artificial intelligence,” Technol Forecast Soc Change, vol. 163, Feb. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120480.
[11] H. Weytjens, E. Lohmann, and M. Kleinsteuber, “Cash flow prediction: MLP and LSTM compared to ARIMA and Prophet,” Electronic Commerce Research, vol. 21, no. 2, pp. 371–391, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.1007/s10660-019-09362-7.
[12] W. Zhu, J. Wu, T. Fu, J. Wang, J. Zhang, and Q. Shangguan, “Dynamic prediction of traffic incident duration on urban expressways: a deep learning approach based on LSTM and MLP,” Journal of Intelligent and Connected Vehicles, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 80–91, Sep. 2021, doi: 10.1108/JICV-03-2021-0004.
[13] B. Yao, “Walmart Sales Prediction Based on Decision Tree, Random Forest, and K Neighbors Regressor,” 2023.
[14] S. Raizada and J. R. Saini, “Comparative Analysis of Supervised Machine Learning Techniques for Sales Forecasting,” International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, vol. 12, no. 11, p. 2021, 2021, doi: 10.14569/IJACSA.2021.0121112.
[15] M. J. A. Shohan, M. O. Faruque, and S. Y. Foo, “Forecasting of Electric Load Using a Hybrid LSTM-Neural Prophet Model,” Energies (Basel), vol. 15, no. 6, Mar. 2022, doi: 10.3390/en15062158.
[16] A. Tasdelen and B. Sen, “A hybrid CNN-LSTM model for pre-miRNA classification,” Sci Rep, vol. 11, no. 1, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93656-0.
[17] M. Ali, D. M. Khan, H. M. Alshanbari, and A. A. A. H. El-Bagoury, “Prediction of Complex Stock Market Data Using an Improved Hybrid EMD-LSTM Model,” Applied Sciences (Switzerland), vol. 13, no. 3, Feb. 2023, doi: 10.3390/app13031429.
[18] M. Mohammadi, S. Jamshidi, A. Rezvanian, M. Gheisari, and A. Kumar, “Advanced fusion of MTM-LSTM and MLP models for time series forecasting: An application for forecasting the solar radiation,” Measurement: Sensors, vol. 33, Jun. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.measen.2024.101179.
[19] R. J. Hyndman and G. Athanasopoulos, Forecasting: Principles and Practice, 3rd ed. OTexts, 2021.
[20] B. Lim and S. Zohren, “Time-series forecasting with deep learning: a survey,” Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, vol. 379, no. 2194, p. 20200209, Apr. 2021, doi: 10.1098/rsta.2020.0209.
[21] T. Mathonsi and T. L. van Zyl, “A Statistics and Deep Learning Hybrid Method for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting and Mortality Modeling,” Forecasting, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1–25, Mar. 2022, doi: 10.3390/forecast4010001.
[22] S. Mohsen, “Recognition of human activity using GRU deep learning algorithm,” Multimed Tools Appl, vol. 82, no. 30, pp. 47733–47749, Dec. 2023, doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-15571-y.
[23] U. M. Sirisha, M. C. Belavagi, and G. Attigeri, “Profit Prediction Using ARIMA, SARIMA and LSTM Models in Time Series Forecasting: A Comparison,” IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 124715–124727, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3224938.
[24] C. C. Izuchukwu Obi, “Demand Forecasting in Retail Business Using the Ensemble Machine Learning Framework-A Stacking Approach,” American Academic Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, vol. 98, no. 1, pp. 309–329, 2024, [Online]. Available: https://asrjetsjournal.org/index.php/American_Scientific_Journal/index
[25] Q. Li and M. Yu, “Achieving Sales Forecasting with Higher Accuracy and Efficiency: A New Model Based on Modified Transformer,” Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 1990–2006, Dec. 2023, doi: 10.3390/jtaer18040100.
[26] G. Woo, C. Liu, D. Sahoo, A. Kumar, and S. Hoi, “ETSformer: Exponential Smoothing Transformers for Time-series Forecasting,” Feb. 2022, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2202.01381
[27] D. Brykin, “Sales Forecasting Models: Comparison between ARIMA, LSTM and Prophet,” Journal of Computer Science, vol. 20, no. 10, pp. 1222–1230, 2024, doi: 10.3844/jcssp.2024.1222.1230.
[28] Hussam Mezher Merdas and Ayad Hameed Mousa, “Food Sales Prediction Using MLP, RANSAC, and Bagging,” Journal of Techniques, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 202–208, Dec. 2023, doi: 10.51173/jt.v5i4.1458.
[29] I. Vallés-Pérez, E. Soria-Olivas, M. Martínez-Sober, A. J. Serrano-López, J. Gómez-Sanchís, and F. Mateo, “Approaching sales forecasting using recurrent neural networks and transformers,” Expert Syst Appl, vol. 201, Sep. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.116993.
[30] N. Qassrawi, M. Azzeh, and M. Hijjawi, “Drug sales forecasting in the pharmaceutical market using deep neural network algorithms,” International Journal of Systematic Innovation, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 63–83, 2024, doi: 10.6977/IJoSI.202409_8(3).0006.
[31] Y. Niu, “Walmart Sales Forecasting using XGBoost algorithm and Feature engineering,” in Proceedings - 2020 International Conference on Big Data and Artificial Intelligence and Software Engineering, ICBASE 2020, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., Oct. 2020, pp. 458–461. doi: 10.1109/ICBASE51474.2020.00103.
[32] A. Bin Tayyab and M. F. Nasim, “WALMART SALES PREDICTION BY USING MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS,” 2024.
[33] Y. F. Akande, J. Idowu, A. Misra, S. Misra, O. N. Akande, and R. Ahuja, “Application of XGBoost Algorithm for Sales Forecasting Using Walmart Dataset,” in Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH, 2022, pp. 147–159. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-1111-8_13.
[34] Y. Liu, “Sales Forecasting Based on Transformer-LSTM Model,” 2024.