- 22 Oct
- 2025
File Tesis Periode 1 2025
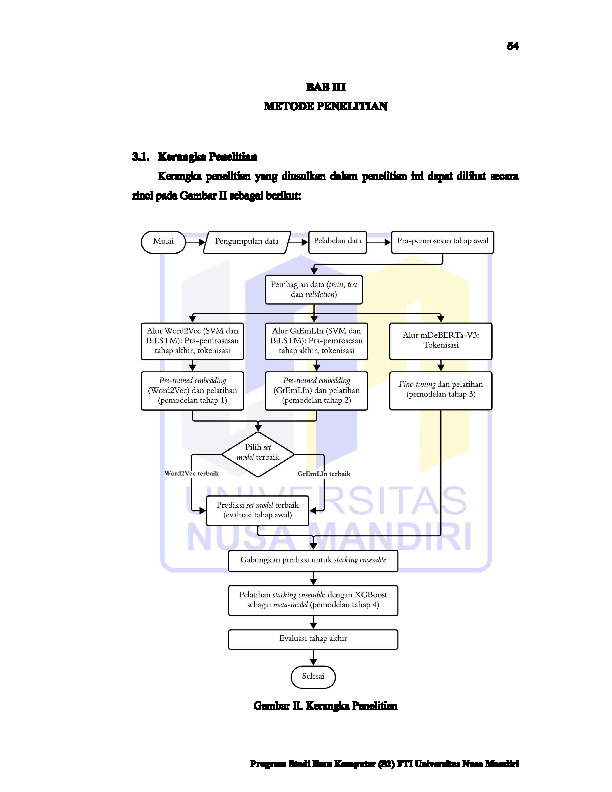
Penelitian ini menganalisis sentimen pengguna aplikasi Taspen Otentikasi menggunakan pemrosesan bahasa alami dan berbagai metode klasifikasi. Data ulasan diambil dari Google Play Store dan dilabeli secara manual. Proses penelitian dilakukan melalui empat tahap yaitu tahap baseline dengan SVM dan BiLSTM menggunakan Word2Vec, tahap SVM dan BiLSTM menggunakan GrEmLIn, tahap fine-tuning model mDeBERTa-v3 dan tahap stacking ensemble menggunakan XGBoost. Evaluasi mencakup akurasi, precision, recall, F1-score dan ROC AUC serta efisiensi komputasi. Model stacking ensemble mencetak akurasi 92,23% dan ROC AUC 0,9594, sementara mDeBERTa-v3 unggul sebagai model tunggal. Embedding GrEmLIn mampu meningkatkan performa BiLSTM berbasis CPU maupun GPU, sedangkan Word2Vec tetap efisien untuk model SVM. Hasil menunjukkan bahwa pemilihan arsitektur dan embedding yang tepat menghasilkan sistem klasifikasi sentimen yang akurat dan efisien untuk layanan digital berbahasa Indonesia.
Unduhan
REFERENSI
[1] P. T. Tbk, “Produk dan Layanan.” Accessed: July 28, 2025. [Online]. Available: http://www.taspen.co.id/produk-layanan
[2] “Apa itu NLP (Natural Language Processing atau Pemrosesan Bahasa Alami)? | IBM.” Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.ibm.com/id-id/think/topics/natural-language-processing
[3] H. Wang, “Word2Vec and SVM Fusion for Advanced Sentiment Analysis on Amazon Reviews,” Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol., vol. 85, pp. 743–749, Mar. 2024, doi: 10.54097/sw4pft19.
[4] J. Xie, B. Chen, X. Gu, F. Liang, and X. Xu, “Self-Attention-Based BiLSTM Model for Short Text Fine-Grained Sentiment Classification,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 180558–180570, 2019, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2957510.
[5] D. Gurgurov, R. Kumar, and S. Ostermann, “GrEmLIn: A Repository of Green Baseline Embeddings for 87 Low-Resource Languages Injected with Multilingual Graph Knowledge,” Jan. 27, 2025, arXiv: arXiv:2409.18193. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2409.18193.
[6] “mdeberta-v3-base | AI Model Details.” Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.aimodels.fyi/models/huggingFace/mdeberta-v3-base-microsoft
[7] “Stacking Ensemble With XGBoost Meta Model (Final Model) | XGBoosting.” Accessed: July 06, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://xgboosting.com/stacking-ensemble-with-xgboost-meta-model-final-model/
[8] “Classification: ROC and AUC | Machine Learning,” Google for Developers. Accessed: Aug. 05, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/classification/roc-and-auc
[9] L. K. Ramasamy, S. Kadry, Y. Nam, and M. N. Meqdad, “Performance analysis of sentiments in Twitter dataset using SVM models,” Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. IJECE, vol. 11, no. 3, p. 2275, June 2021, doi: 10.11591/ijece.v11i3.pp2275-2284.
[10] A. S. Rahayu and A. Fauzi, “Komparasi Algoritma Naïve Bayes Dan Support Vector Machine (SVM) Pada Analisis Sentimen Spotify,” vol. 4, 2022.
[11] S. D. Anggita and F. F. Abdulloh, “Optimasi Algoritma Support Vector Machine Berbasis PSO Dan Seleksi Fitur Information Gain Pada Analisis Sentimen,” vol. 4, no. 1, 2023.
[12] Shahmirul Hafizullah Imanuddin, Kusworo Adi, and Rahmat Gernowo, “Sentiment Analysis on Satusehat Application Using Support Vector Machine Method,” J. Electron. Electromed. Eng. Med. Inform., vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 143–149, July 2023, doi: 10.35882/jeemi.v5i3.304.
[13] M. Umar, N. B. Ahmad, and A. Zainal, “Sentiment Analysis of Student’s Opinion on Programming Assessment: Evaluation of Naïve Bayes over Support Vector Machines,” Int. J. Innov. Comput., vol. 10, no. 2, Nov. 2020, doi: 10.11113/ijic.v10n2.278.
[14] A. K. Laturiuw and Y. A. Singgalen, “Sentiment Analysis of Raja Ampat Tourism Destination Using CRISP-DM: SVM, NBC, DT, and k-NN Algorithm,” J. Inf. Syst. Inform., vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 518–535, May 2023, doi: 10.51519/journalisi.v5i2.490.
[15] B. A. Ardhani, N. Chamidah, and T. Saifudin, “Sentiment Analysis Towards Kartu Prakerja Using Text Mining with Support Vector Machine and Radial Basis Function Kernel,” J. Inf. Syst. Eng. Bus. Intell., vol. 7, no. 2, p. 119, Oct. 2021, doi: 10.20473/jisebi.7.2.119-128.
[16] S. Wang, Y. Zhu, W. Gao, M. Cao, and M. Li, “Emotion-Semantic-Enhanced Bidirectional LSTM with Multi-Head Attention Mechanism for Microblog Sentiment Analysis,” Information, vol. 11, no. 5, p. 280, May 2020, doi: 10.3390/info11050280.
[17] R. Ranjan and D. A. K., “An Optimized Deep ConvNet Sentiment Classification Model with Word Embedding and BiLSTM Technique,” ADCAIJ Adv. Distrib. Comput. Artif. Intell. J., vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 309–329, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.14201/adcaij.27902.
[18] V. K. Agbesi, C. Wenyu, C. C. Ukwuoma, N. A. Kuadey, J. A. Browne, and I. O. Agyemang, “Multi-Channel 2D-CNN And Attention-Based BiLSTM Method for Sentiment Analysis on Low-Resource Ewe Language,” Nov. 04, 2022, In Review. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2221141/v1.
[19] Y. Mao, Y. Zhang, L. Jiao, and H. Zhang, “Document-Level Sentiment Analysis Using Attention-Based Bi-Directional Long Short-Term Memory Network and Two-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network,” Electronics, vol. 11, no. 12, p. 1906, June 2022, doi: 10.3390/electronics11121906.
[20] J. Khan, N. Ahmad, S. Khalid, F. Ali, and Y. Lee, “Sentiment and Context-Aware Hybrid DNN With Attention for Text Sentiment Classification,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 28162–28179, 2023, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3259107.
[21] Z. Tao and Z. Wu, “Sentiment Analysis of Product Reviews Based on Bi-LSTM and Max Pooling,” in Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications, C. Chen, Ed., IOS Press, 2024. doi: 10.3233/FAIA231407.
[22] Y. Zhou, Q. Zhang, D. Wang, and X. Gu, “Text Sentiment Analysis Based on a New Hybrid Network Model,” Comput. Intell. Neurosci., vol. 2022, pp. 1–15, Dec. 2022, doi: 10.1155/2022/6774320.
[23] B. A. Chandio, A. S. Imran, M. Bakhtyar, S. M. Daudpota, and J. Baber, “Attention-Based RU-BiLSTM Sentiment Analysis Model for Roman Urdu,” Appl. Sci., vol. 12, no. 7, p. 3641, Apr. 2022, doi: 10.3390/app12073641.
[24] N. Chen, Y. Sun, and Y. Yan, “Sentiment analysis and research based on two‐channel parallel hybrid neural network model with attention mechanism,” IET Control Theory Appl., vol. 17, no. 17, pp. 2259–2267, Nov. 2023, doi: 10.1049/cth2.12463.
[25] P. He, X. Liu, J. Gao, and W. Chen, “DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention,” Oct. 06, 2021, arXiv: arXiv:2006.03654. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2006.03654.
[26] A. Aziz, Md. A. Hossain, and A. N. Chy, “CSECU-DSG at SemEval-2023 Task 4: Fine-tuning DeBERTa Transformer Model with Cross-fold Training and Multi-sample Dropout for Human Values Identification,” in Proceedings of the The 17th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2023), Toronto, Canada: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2023, pp. 1988–1994. doi: 10.18653/v1/2023.semeval-1.274.
[27] F. Hassan, A. Bouchekif, and W. Aransa, “FiRC at SemEval-2023 Task 10: Fine-grained Classification of Online Sexism Content Using DeBERTa,” in Proceedings of the The 17th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2023), Toronto, Canada: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2023, pp. 1824–1832. doi: 10.18653/v1/2023.semeval-1.252.
[28] P. He, J. Gao, and W. Chen, “DeBERTaV3: Improving DeBERTa using ELECTRA-Style Pre-Training with Gradient-Disentangled Embedding Sharing,” Mar. 24, 2023, arXiv: arXiv:2111.09543. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2111.09543.
[29] S. Mahendru and T. Pandit, “SecureNet: A Comparative Study of DeBERTa and Large Language Models for Phishing Detection,” in 2024 IEEE 7th International Conference on Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (BDAI), July 2024, pp. 160–169. doi: 10.1109/BDAI62182.2024.10692765.
[30] P. Kandru, B. Singh, A. Maity, K. Aditya Hari, and V. Varma, “Tenzin-Gyatso at SemEval-2023 Task 4: Identifying Human Values behind Arguments Using DeBERTa,” in Proceedings of the The 17th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2023), Toronto, Canada: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2023, pp. 2062–2066. doi: 10.18653/v1/2023.semeval-1.284.
[31] W. Zhong, “Effectiveness of finetuning pretrained BERT and deBERTa for automatic essay scoring,” Appl. Comput. Eng., vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 87–95, Mar. 2024, doi: 10.54254/2755-2721/52/20241321.
[32] M. Younes, A. Kharabsheh, and M. B. Younes, “Alexa at SemEval-2023 Task 10: Ensemble Modeling of DeBERTa and BERT Variations for Identifying Sexist Text”.
[33] W. Yee Wong et al., “A Stacked Ensemble Deep Learning Approach for Imbalanced Multi-Class Water Quality Index Prediction,” Comput. Mater. Contin., vol. 76, no. 2, pp. 1361–1384, 2023, doi: 10.32604/cmc.2023.038045.
[34] A. Gaius, R. W. Mwangi, and A. Ngunyi, “A Stacking-Based Ensemble Approach with Embeddings from Language Models for Depression Detection from Social Media Text,” J. Data Anal. Inf. Process., vol. 11, no. 04, pp. 420–453, 2023, doi: 10.4236/jdaip.2023.114022.
[35] S. Zian, S. A. Kareem, and K. D. Varathan, “An Empirical Evaluation of Stacked Ensembles With Different Meta-Learners in Imbalanced Classification,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 87434–87452, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3088414.
[36] M. S. SIVRI, “Combining Sentiment Analysis Models Using Stacking Ensemble Learning Techniques on BIST30 Stocks,” Oct. 2024, doi: 10.5281/ZENODO.13996517.
[37] M. A. Ganaie, M. Hu, A. K. Malik, M. Tanveer, and P. N. Suganthan, “Ensemble deep learning: A review,” Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell., vol. 115, p. 105151, Oct. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105151.
[38] K. Azim et al., “Ensemble stacked model for enhanced identification of sentiments from IMDB reviews,” Sci. Rep., vol. 15, no. 1, p. 13405, Apr. 2025, doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97561-8.
[39] Z. Arif Ali, Z. H. Abduljabbar, H. A. Tahir, A. Bibo Sallow, and S. M. Almufti, “Exploring the Power of eXtreme Gradient Boosting Algorithm in Machine Learning: a Review,” Acad. J. Nawroz Univ., vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 320–334, May 2023, doi: 10.25007/ajnu.v12n2a1612.
[40] S. D. A. Rihan, M. Anbar, and B. A. Alabsi, “Meta-Learner-Based Approach for Detecting Attacks on Internet of Things Networks,” Sensors, vol. 23, no. 19, p. 8191, Sept. 2023, doi: 10.3390/s23198191.
[41] D. A. Al-Qudah, A. M. Al-Zoubi, A. I. Cristea, J. J. Merelo-Guervós, P. A. Castillo, and H. Faris, “Prediction of sentiment polarity in restaurant reviews using an ordinal regression approach based on evolutionary XGBoost,” PeerJ Comput. Sci., vol. 11, p. e2370, Jan. 2025, doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2370.
[42] W. Bakasa and S. Viriri, “Stacked ensemble deep learning for pancreas cancer classification using extreme gradient boosting,” Front. Artif. Intell., vol. 6, p. 1232640, Oct. 2023, doi: 10.3389/frai.2023.1232640.
[43] J. Jasmir, W. Riyadi, S. R. Agustini, Y. Arvita, D. Meisak, and L. Aryani, “Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory and Word Embedding Feature for Improvement Classification of Cancer Clinical Trial Document,” J. RESTI Rekayasa Sist. Dan Teknol. Inf., vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 505–510, Aug. 2022, doi: 10.29207/resti.v6i4.4005.
[44] L. N. Aqilla, Y. Sibaroni, and S. S. Prasetiyowati, “Word2vec Architecture in Sentiment Classification of Fuel Price Increase Using CNN-BiLSTM Method,” Sinkron, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 1654–1664, July 2023, doi: 10.33395/sinkron.v8i3.12639.
[45] A. E., A. F., and N. A., “Automated Essay Scoring using Word2vec and Support Vector Machine,” Int. J. Comput. Appl., vol. 177, no. 25, pp. 20–29, Dec. 2019, doi: 10.5120/ijca2019919707.
[46] G. Gritsay, A. Grabovoy, A. Kildyakov, and Y. Chekhovich, “Automated Text Identification: Multilingual Transformer-based Models Approach”.
[47] H. T. Ta, A. B. S. Rahman, L. Najjar, and A. Gelbukh, “Transfer Learning from Multilingual DeBERTa for Sexism Identification”.
[48] Z. Feng et al., “KDD CUP 2022 MULTICLASS PRODUCT CLASSIFICATION: TEAM MetaSoul SOLUTION,” 2022.
[49] F. Xia et al., “LingJing at SemEval-2022 Task 3: Applying DeBERTa to Lexical-level Presupposed Relation Taxonomy with Knowledge Transfer,” in Proceedings of the 16th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2022), Seattle, United States: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2022, pp. 239–246. doi: 10.18653/v1/2022.semeval-1.30.
[50] L. Saragih, M. Nababan, Y. Simatupang, and J. Amalia, “ANALISIS SELF-ATTENTION PADA BI-DIRECTIONAL LSTM DENGAN FASTTEXT DALAM MENDETEKSI EMOSI BERDASARKAN TEXT,” ZONAsi J. Sist. Inf., vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 144–156, Nov. 2022, doi: 10.31849/zn.v4i2.10846.
[51] Michael Nnaemeka Ajemba and Ebube Chinwe Arene, “Research gaps for future research and their identification,” World J. Adv. Res. Rev., vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 575–579, Oct. 2022, doi: 10.30574/wjarr.2022.16.1.1062.
[52] P. T. Tbk, “Profil Perusahaan.” Accessed: July 28, 2025. [Online]. Available: http://www.taspen.co.id/tentang-taspen/profil-perusahaan
[53] P. T. Tbk, “Nilai Perusahaan.” Accessed: July 28, 2025. [Online]. Available: http://www.taspen.co.id/tentang-taspen/nilai-perusahaan
[54] “Google Play,” Wikipedia bahasa Indonesia, ensiklopedia bebas. Jan. 06, 2025. Accessed: July 28, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://id.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Google_Play&oldid=26758609
[55] P. T. Tbk, “Layanan Lainnya.” Accessed: July 28, 2025. [Online]. Available: http://www.taspen.co.id/produk-layanan/layanan-lainnya
[56] “Data Mining Tutorial,” GeeksforGeeks. Accessed: Aug. 05, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/data-science/data-mining/
[57] M. A. Palomino and F. Aider, “Evaluating the Effectiveness of Text Pre-Processing in Sentiment Analysis,” Appl. Sci., vol. 12, no. 17, p. 8765, Aug. 2022, doi: 10.3390/app12178765.
[58] K. Patel, “Text to Numeric Representation in NLP: A Beginner-Friendly Guide,” Medium. Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://medium.com/@ketan.patel_46870/text-to-numeric-representation-in-nlp-a-beginner-friendly-guide-9e68c8f8d07c
[59] “The Beginner’s Guide to Text Embeddings | deepset Blog.” Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.deepset.ai/blog/the-beginners-guide-to-text-embeddings
[60] S. Lee, “Word2Vec: The Power of Word Embeddings.” Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/word2vec-power-of-word-embeddings
[61] “Word Embedding using Word2Vec - GeeksforGeeks.” Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python/python-word-embedding-using-word2vec/
[62] “What are Word Embeddings? | A Comprehensive Word Embedding Guide.” Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.elastic.co/what-is/word-embedding
[63] J. Canary, “Transfer Learning: Leveraging Pretrained Models,” Medium. Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://medium.com/@jimcanary/transfer-learning-leveraging-pretrained-models-153ab99b9b00
[64] “Support Vector Machine - Definition and Benefits.” Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.lyzr.ai/glossaries/support-vector-machine/
[65] T. DigitalDefynd, “10 Pros & Cons of Support Vector Machines [2025],” DigitalDefynd. Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://digitaldefynd.com/IQ/pros-cons-of-support-vector-machines/
[66] “Bidirectional LSTM in NLP - GeeksforGeeks.” Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/nlp/bidirectional-lstm-in-nlp/
[67] J. O. Schneppat, “Bidirectional Long-Short Term Memory (BiLSTM),” Schneppat AI. Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://schneppat.com/bidirectional-long-short-term-memory_bilstm.html
[68] “Self - Attention in NLP,” GeeksforGeeks. Accessed: Aug. 05, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/nlp/self-attention-in-nlp/
[69] D. Jones, “Ensemble Learning: Combining Models for Better Machine Learning,” Medium. Accessed: Aug. 05, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://medium.com/@duygujones/ensemble-learning-combining-models-for-better-machine-learning-d75d7be66b10
[70] “What is XGBoost?,” NVIDIA Data Science Glossary. Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/glossary/xgboost/
[71] Kamus Bahasa Indonesia. Pusat Bahasa Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, 2008.
[72] itsmeSamrat, “Splitting the Data to 60–20–20 ratio vs. 80–10–10. Which one is better?,” Medium. Accessed: Aug. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://medium.com/@itsmeSamrat/splitting-the-data-to-60-20-20-ratio-vs-80-10-10-which-one-is-better-bbc3503830d8
[73] “How to explain the ROC AUC score and ROC curve?” Accessed: Aug. 03, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.evidentlyai.com/classification-metrics/explain-roc-curve