- 15 Dec
- 2020
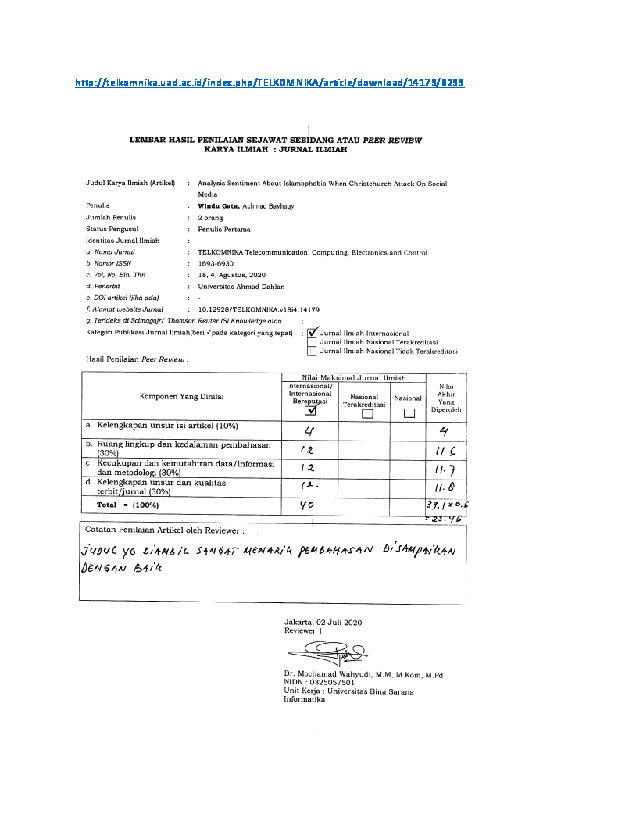
Analysis sentiment about islamophobia when Christchurch attack on social media
Islamophobia is formed by "Islam" with "-phobia" which means "fear of Islam". This shows the view of Islam as "other" and can threaten Western culture. The recent horrific terror attack that took place at the Christchurch mosque in New Zealand, is the result of allowing an attitude of hatred towards Islam in the West. Twitter is social media that allows users send real-time messages and can be used for sentiment analysis because it has a large amount of data. The lexical based method using VADER is used for automatic labeling of crawling data from Twitter. And then compare supervised machine learning Naïve Bayes and SVM algorithm. Addition of SMOTE for imbalanced data. As result, SVM with SMOTE is proven the highest performance value and short processing time.
Unduhan
-
Analysis Sentiment About Islamophobia.pdf
Terakhir download 20 Feb 2026 13:02peer review Analysis sentiment about islamophobia when Christchurch attack on social media
- diunduh 239x | Ukuran 108 KB
-
295539406.pdf
Terakhir download 28 Feb 2026 02:02Analysis sentiment about islamophobia when Christchurch attack on social media
- diunduh 535x | Ukuran 982 KB
-
295539406.pdf
Terakhir download 28 Feb 2026 02:02Analysis sentiment about islamophobia when Christchurch attack on social media
- diunduh 535x | Ukuran 1,005,972
-
dokumen - telkomnika - Analysis sentiment about islamophobia when Christchurch attack on social media - full.pdf
Terakhir download 27 Feb 2026 10:02jurnal, proses, dan penilaian jurna
- diunduh 98x | Ukuran 1,669,316
REFERENSI
[1] G. Evolvi, “Hate in a Tweet: Exploring Internet-Based Islamophobic Discourses,” Religions, 2018. doi: 10.3390/rel9100307. [2] C. Wood and W. M. L. Finlay, “British national party representations of muslims in the month after the London bombings: Homogeneity, threat, and the conspiracy tradition,” Br. J. Soc. Psychol., vol. 47, pp. 407-26, doi: 10.1348/014466607X264103. [3] C. Allen, “Britain First: The ‘Frontline Resistance’ to the Islamification of Britain,” The Political Quarterly, vol. 85, no. 3, 2014, doi: 10.1111/1467-923X.12118. [4] M. Ekman, “Online Islamophobia and the politics of fear: manufacturing the green scare,” JournalEthnic and Racial Studies, vol. 38, no. 11, pp. 1986-2002, 2014. [5] N. Bakali, “Islamophobia in Quebec secondary schools: Inquiries into the experiences of muslim male youth post-9/11,” in Muslim Students, Education and Neoliberalism: Schooling a “Suspect Community,” 2017. [6] I. Awan and I. Zempi, “The affinity between online and offline anti-Muslim hate crime: Dynamics and impacts,” Aggression and Violent Behavior, vol. 27, no. 1-8, 2016. [7] Nurcholis, “Dunia Sebut Teror Masjid Kembar Selandia Baru Dampak Islamophobia, in Bahasa: The World Called the Terror of the Twin Towers of New Zealand the Impact of Islamophobia,” Indonesiainside.id, 2019. [8] A. Brown, “What is so special about online (as compared to offline) hate speech?,” Ethnicities, 2018. doi: 10.1177/1468796817709846. [9] B. Liu, "Sentiment Analysis: A Fascinating Problem," Synthesis Lectures on Human Language Technilogies, 2012. [10] B. Vidgen and T. Yasseri, “Detecting weak and strong Islamophobic hate speech on social media,” Journal of Information Technology & Politics, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 66-78, 2019. [11] K. Darwish, W. Magdy, A. Rahimi, T. Baldwin, and N. Abokhodair, “Predicting Online Islamophobic Behavior after #ParisAttacks,” J. Web Sci., vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 34-52, 2018. [12] J. Ramteke, S. Shah, D. Godhia, and A. Shaikh, “Election result prediction using Twitter sentiment analysis,” 2016 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), pp. 1-5, 2016. [13] A. Bayhaqy, Sfenrianto, K. Nainggolan, and E. Kaburuan, “Sentiment Analysis about E-Commerce from Tweets Using Decision Tree, K-Nearest Neighbor, and Naïve Bayes,” 2018 International Conference on Orange Technologies (ICOT), 2018. [14] N. D. Pratama, Y. A. Sari, and P. P. Adikara, “Analisis Sentimen Pada Review Konsumen Menggunakan Metode Naïve Bayes Dengan Seleksi Fitur Chi Square Untuk Rekomendasi Lokasi Makanan Tradisional, in Bahasa: Sentiment Analysis on Consumer Reviews Using the Naïve Bayes Method with Chi Square Feature Selection for Recommended Locations of Traditional Foods,” J. Pengemb. Teknol. Inf. dan Ilmu Komput. Univ. Brawijaya, vol. 2, no. 9, pp. 2982-2988, 2018. [15] A. C. Flores, R. I. Icoy, C. F. Pena, and K. D. Gorro, “An Evaluation of SVM and Naïve Bayes with SMOTE on Sentiment Analysis Data Set,” 2018 International Conference on Engineering, Applied Sciences, and Technology (ICEAST), pp. 1-4, 2018. [16] K. A. Beydoun, "American Islamophobia: Understanding the Roots and Rise of Fear, 1st ed," Oakland: University of California Press, 2018. [17] N. M. S. Hadna, P. I. Santosa, and W. W. Winarno, “Studi Literatur Tentang Perbandingan Metode untuk Proses Analisis Sentimen di Twitter, in Bahasa: Literature Study of Comparative Methods for Sentiment Analysis Process on Twitter” Semin. Nas. Teknol. Inf. dan Komun., vol. 2016, no. Sentika, pp. 57-64, 2016. [18] E. T. L. Kusrini, "Algoritma Data Mining," Yogyakarta: Andi, 2009. [19] T. Jo, "Text Mining Concepts, Implementation, and Big Data Challenge," Studies in Big Data, 2019. [20] S. Symeonidis, “5 Things You Need to Know about Sentiment Analysis and Classification,” KDnuggets, 2018. [21] C. J. Hutto, “VADER-Sentiment-Analysis,” Eighth International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media (ICWSM-14), 2014. [22] Alberto Fernandez, Salvador Garcia, Francisco Herrera, and Nitesh V. Chawla, “SMOTE for Learning from Imbalanced Data: Progress and Challenges, Marking the 15-year Anniversary,” J. Artif. Intell. Res., vol. 61, no. 1, pp. 863-905, 2018. [23] S. R. Wicaksono, "Studi Kasus Sistem Berbasis Pengetahuan: Membahas Metode ID3, Naïve Bayes dan Certainty Factor, in Bahasa: Case Study of Knowledge Based Systems: Discusses the ID3 Method, Naïve Bayes and Certainty Factor," Seribu Bintang, 2018. [24] R. M. Gaba Ignatow, "An Introduction to Text Mining: Research Design, Data Collection and Analysis," United States of A: SAGE Publications, Inc, 2017. [25] N. K. Wardhani et al., “Sentiment analysis article news coordinator minister of maritime affairs using algorithm Naïve bayes and support vector machine with particle swarm optimization,” J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol., vol. 96, no. 24, pp. 8365-8378, 2018. [26] V. Kotu and B. Deshpande, "Predictive Analytics and Data Mining: Concepts and Practice with RapidMiner," Morgan Kaufmann, 2015. [27] K. Sigit, A. P. Dewi, G. Windu, Nurmalasari, T. Muhamad, and N. Kadinar, “Comparison Of Classification Methods On Sentiment Analysis Of Political Figure Electability Based On Public Comments On Online News Media Sites,” IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 662, no. 4, 2019.