- 15 Dec
- 2020
Specify of Estimation Using C4.5 Algorithm of Software Project Estimation at the Point of Sales Application with Cocomo II
In software development, it is required an appropriate estimate. One of the most commonly used software project estimation models is Constructive Cost Model(COCOMO II). The model is often used to obtain accurate results in estimating important factors such as cost and human resources. However, to obtain the more accurate estimation results, this study proposes a C4.5 algorithm based on COCOMO II estimation results. In this study, software project estimates are used in the Point of Sales (POS) applications. Based on these data with COCOMO II method, it is estimated that the schedule, staff, and cost are also specifying estimation from the result of COCOMO II using a C4.5 algorithm. The accuracy of the estimation results is around 90% with Algorithm C4.5. The value can be used as a reference for the development of the next POS software project.
Unduhan
-
Specify of Estimation Using C45.pdf
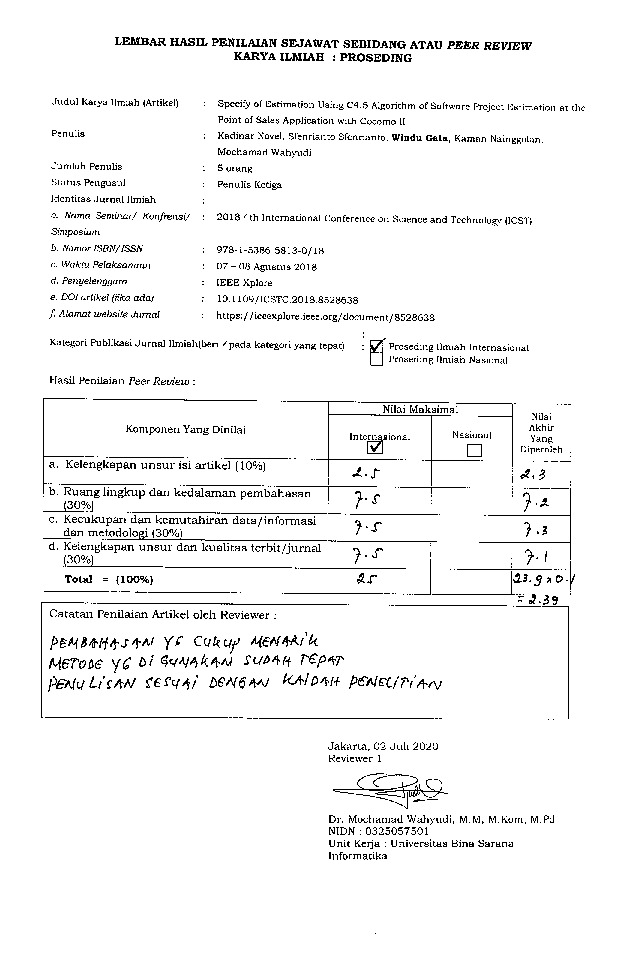
Terakhir download 25 Feb 2026 13:02peer review Specify of Estimation Using C4.5 Algorithm of Software Project Estimation at the Point of Sales Application with Cocomo II
- diunduh 208x | Ukuran 108 KB
-
Specify of Estimation Using C4.5 Algorithm of.pdf
Terakhir download 27 Feb 2026 17:02Specify of Estimation Using C4.5 Algorithm of Software Project Estimation at the Point of Sales Application with Cocomo II
- diunduh 741x | Ukuran 580 KB
-
Specify of Estimation Using C4.5 Algorithm of.pdf
Terakhir download 27 Feb 2026 17:02Specify of Estimation Using C4.5 Algorithm of Software Project Estimation at the Point of Sales Application with Cocomo II
- diunduh 741x | Ukuran 594,332
-
2018 Estimation_at_the_Point_of_Sales_Application_with_Cocomo_II.pdf.pdf
Terakhir download 25 Feb 2026 17:02turnitin Specify of Estimation Using C4.5 Algorithm of Software Project Estimation at the Point of Sales Application with Cocomo II
- diunduh 416x | Ukuran 1,740,792
REFERENSI
[1] T. N. Sharma"Analysis of software cost estimation using COCOMO II." International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research 2.6 (2011): pp. 1-5. [2] J. Živadinović, Z. Medić, D. Maksimović, A. Damnjanović, & S. Vujčić Methods of effort estimation in software engineering. In International Symposium Engineering Management and Competitiveness. (2011, June), Zrenjanin, Serbia. [3] R. Dillibabu, and K. Krishnaiah. "Cost estimation of a software product using COCOMO II. 2000 model–a case study."International Journal of Project Management, vol.23, no.4, pp. 297-307, 2005. [4] X. Huang, D. Ho, J. Ren, and L. F. Capretz, L.F. Improving the COCOMO Model using a NeuroFuzzy Approach, Applied Soft Computing, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 29-40, 2011. [5] Q. Song, M. Shepperd, X. Chen, and J. Liu. Can KNN imputation improve the performance of C4.5 with small software project data sets? A comparative evaluation, The Journal of Systems and Software, vol. 81, pp. 2361-2370, 2008. [6] F. S Gharehchopogh, I. Maleki, A. Kamalinia, and H. M. Zadeh, Artificial bee colony based constructive cost model for software cost estimation. Journal of Scientific Research and Development, Vo. 1, no. 2, pp. 44-51, 2014. [7] K. Mao, Y. Yang, M. Li, and M. Harman, Pricing crowdsourcing-based software development tasks. In Proceedings of the 2013 international conference on Software engineering, pp. 1205-1208, (2013, May, IEEE Press. [8] M. Chemuturi, Software Estimation Best Practices, Tools & Techniques: A Complete Guide for Software Project Estimators, 2009, USA: J. Ross Publishing. [9] F. S Gharehchopogh, Neural networks application in software cost estimation: a case study. In Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications (INISTA), 2011 International Symposium on , pp. 69-73), IEEE. [10] T. Zimmermann, N. Nagappan, H. Gall, E. Giger, and B. Murphy,. Cross-project defect prediction: a large scale experiment on data vs. domain vs. process. In Proceedings of the the 7th joint meeting of the European software engineering conference and the ACM SIGSOFT symposium on The foundations of software engineering, (2009, August) , pp. 91-100), ACM [11] Sfenrianto, P. Indah, and R. Broer, Naïve Bayes Classifier Algorithm Particle Swam optimization for classification of Cross Selling (Case study: PT. TELKOM Jakarta), Cyber and IT Service Management, International Conference on IEEE, 2016. [12] A. M. Langer Analysis and Design of Information Systems (3rded). 2008. London: Springer,. [13] M. Al Yahya, R. Ahtnad, and S. Lee. “Impact of CMMI Based Software Process Maturity on COCOMO II’s Effort Estimation”. The International Arab Journal of Information Technology. vol. 7. No. 2. April 2010. [14] Khatibi,Vahid andN. A. Jawawi, Dayang. “Software Cost Estimation Methods: A Review”. Journal of Emerging Trends in Computing and Information Sciences. Volume 2 No. 1 2010. ISSN 2079-8407 [15] Boehm, B., 2001. Software Cost Estimation with COCOMO II. [16] Nofriansyah, Dicky.Konsep Data Mining Vs Sistem Pendukung Keputusan. 2014, Yogyakarta: Deepublish. [17] Damayanti, D. E. Suprapto, Kusuma, and A. R. Perdana. Analisis Estimasi Biaya Pembuatan Perangkat Lunak Menggunakan Metode COCOMO II di Inagata Technosmith (Studi Kasus : Sistem Informasi Monitoring dan Evaluasi Penerimaan Beasiswa Santri Berprestasi UIN Malang). Jurnal Pengembangan Teknologi Informasi dan Ilmu Komputer, Vol. 1, No. 10, 2017 (e-ISSN: 2548-964X). [18] Primaraka, A. Handoyo, E. Isnanto, and Rizal. “Estimasi Biaya Pembuatan Perangkat Lunak Menggunakan Metode Cocomo II Pada Sistem Informasi Pelaporan Kegiatan Pembangunan,” (Project report), 2011.